The federal government is abandoning its role in providing critical social safety nets, advocates and policy watchers warned.
The Senate reconciliation bill would cut $186 billion from the Supplemental Nutrition Assistance Program (SNAP) over the next decade, according to the Congressional Budget Office. It would be the largest cut in the program’s history. SNAP, known as CalFresh in California, provides low income families a stipend every month for groceries. The cuts would push the onus on states to shoulder some benefit costs—a departure from how the program traditionally has worked—and impose work requirements on certain adults. The bill is now with the House of Representatives for a final vote before reaching Trump’s desk.
In Santa Clara County, where CalFresh participation is at its highest level in the past decade, these cuts would mean some families could lose their benefits if the state can’t fill in the gap. Overall, cuts to food stamps, Medi-Cal, housing vouchers and more could cost Santa Clara County up to $1 billion in federal funding.
“The bill proposes changes to eligibility that will make it harder for families to access benefits while also shifting a significant portion of costs to states—costs that are simply untenable for state and local governments to absorb,” County Executive James Williams told San José Spotlight. “Food is essential to survival…we are profoundly concerned about what these unprecedented cuts mean for so many families in our community, and we are continuing to evaluate impacts to our community.”
As of last July, the federally funded food assistance program has more than 130,000 individuals receiving food stamps in the county, almost double what it was in 2019, according to CalFresh data.
Some 5.3 million Californians in 2024 received an average of $189 per month in food stamps, totaling $12 billion. Trump’s bill would cut the state’s CalFresh’s funding down between $5.4 billion to $2.8 billion, resulting in more than 735,000 people losing their benefits, according to the governor’s office.
Traditionally, the federal government covered food stamp benefits while costs of administering the program is shared by counties, states and the federal government. This formula works since the federal government can operate at a deficit and print money when needed, unlike state governments.
Fullwell Executive Director Eli Zigas operates a Bay Area nonprofit that creates policies to tackle food insecurity in the state. He said requiring states to cover anywhere from 5% to 25% of the benefits means cuts are inevitable.
“The federal government is walking away from its commitment to fully fund this program, and they’re pushing some of the costs onto the states without really caring whether the states can handle it,” Zigas told San José Spotlight. “Or they know that the states can’t handle it, and therefore they’ll see a reduction in the number of people receiving assistance.”
California provides assistance
While the federal government continues to pare back money for these vital resources, the California Legislature is trying to bolster some programs in a difficult budget year. Included in the state’s budget for this new fiscal year is $36 million for the CalFresh Fruit and Vegetable Program, a pilot program which allows people with EBT cards to receive instant rebates up to $60 a month when buying produce at select grocery stores.
“It’s more money than the program’s ever received,” Zigas said. “It’s an example of California providing some money to boost the safety net, but the magnitude of the SNAP cuts dwarfs that.”
The state also added $60 million for CalFood, a program that allows food banks to purchase California-grown foods for the communities they serve. Many food banks use these dollars to buy more expensive items like eggs.
“We are incredibly grateful to the governor and legislature for the $60 million in CalFood, which will help food banks serve over 6 million Californians each month,” Itzúl Gutierrez, senior policy advocate with the California Association of Food Banks, told San José Spotlight. “However, if these devastating cuts to SNAP in the Budget Reconciliation bill get passed, food banks will not be able to fill the gap. For every meal that a food bank provides, SNAP provides nine,” Gutierrez said.
During times of food insecurity, families turn to food banks for assistance—and food banks will see longer lines as people lose CalFresh benefits. However, food banks are already being stretched to the limit.
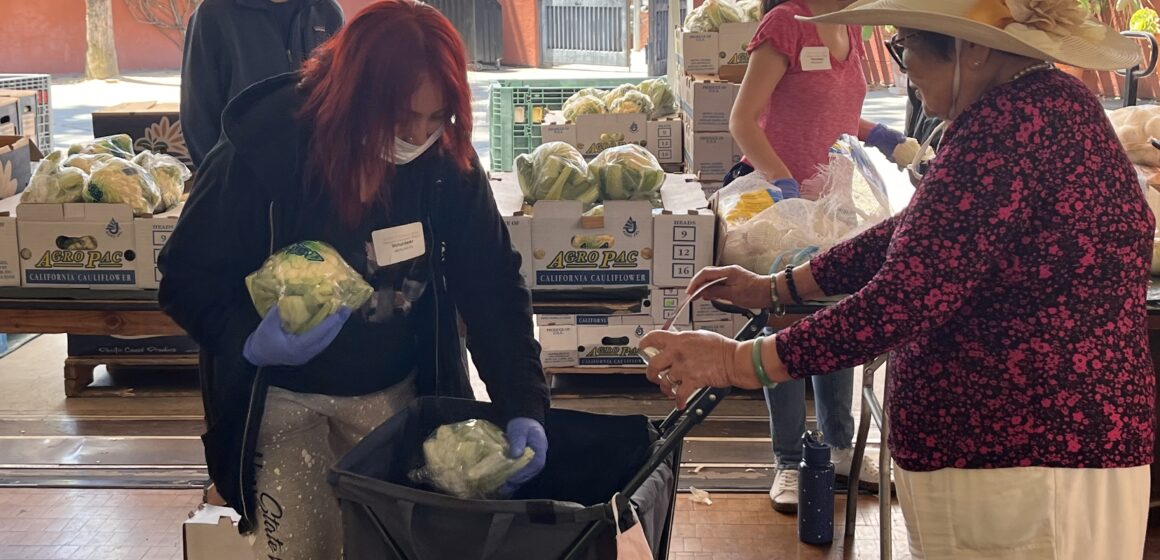
Second Harvest of Silicon Valley serves approximately 500,000 people a month in Santa Clara and San Mateo counties — the same number as during the height of the pandemic. Prior to that, the food bank served 250,000 people every month through food distributions and grocery programs.
“In our two counties alone, people receive about 32 million in benefits (from CalFresh) a month,” Second Harvest CEO Leslie Bacho told San José Spotlight. “So those are dollars that people are spending in our local grocery stores. And so the cuts will have an impact, not just on individuals, but also on our local economy.
“Editor’s note: A previous version of this story included lower projected cuts prior to the passing of the ‘Big Beautiful Bill’.
Contact Joyce Chu at [email protected] or @joyce_speaks on X.



Leave a Reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.